
Knitting is a wonderful hobby that allows you to create unique and personalized items. However, if you’re new to knitting, understanding knitting patterns can be quite intimidating. They are filled with abbreviations, symbols, and instructions that may seem like an entirely different language. But don’t worry! With a little guidance, you’ll soon be able to decipher and follow knitting patterns with ease.
Knitting patterns serve as a roadmap for your project, providing step-by-step instructions on how to create a specific item. They include details about the materials you’ll need, the gauge, stitch patterns, and finishing techniques. Understanding the structure and terminology used in knitting patterns is the key to becoming a confident knitter.
First and foremost, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the abbreviations commonly used in knitting patterns. From K (knit) and P (purl) to YO (yarn over) and BO (bind off), each abbreviation represents a specific knitting stitch or technique. By knowing these abbreviations, you’ll be able to read patterns more fluently and quickly understand the instructions.
How to Read Knitting Patterns for Beginners
Knitting patterns can sometimes seem confusing and overwhelming to beginners. However, with a little practice and understanding, you’ll be able to read knitting patterns like a pro. Here are some tips to help you get started.
1. Familiarize Yourself with Common Abbreviations
Knitting patterns often use abbreviations to save space and make the instructions easier to read. Before you start reading a pattern, make sure you know the common abbreviations. This will help you understand the instructions better and knit with confidence. Some common abbreviations include K (knit), P (purl), CO (cast on), and BO (bind off).
2. Read the Materials and Gauge Section First
Before diving into the pattern instructions, read the materials and gauge section. This section will provide you with important information about the type and quantity of yarn, needle size, and gauge required for the project. Paying attention to gauge is crucial, as it ensures that your finished project will turn out the right size.
3. Break It Down Step by Step

When reading a knitting pattern, it’s helpful to break it down step by step. Start by reading the first row or round of instructions and make sure you understand what each step is asking you to do. Then, move on to the next row or round and repeat the process. Breaking down the pattern into smaller steps will make it less overwhelming and easier to follow.
Remember, knitting patterns are like a roadmap that guide you through the creation of a knitted item. With practice and patience, you’ll become more comfortable with reading patterns and be able to take on more complex knitting projects.
Understanding Stitch Abbreviations
When reading a knitting pattern, you will encounter various stitch abbreviations. These abbreviations are used to make the instructions more concise and easier to follow. Understanding these abbreviations is essential for successfully completing the pattern.
Here are some common stitch abbreviations that you may come across:
- K: Knit stitch.
- P: Purl stitch.
- K2tog: Knit two stitches together.
- P2tog: Purl two stitches together.
- YO: Yarn over, which creates an extra stitch by wrapping the yarn around the needle.
- SSK: Slip, slip, knit. Slip two stitches one by one as if to knit, then knit them together through the back loops.
In addition to these basic stitch abbreviations, there are also variations and combinations of stitches that may be used in a pattern. It’s important to refer to the pattern’s glossary or key to understand any unique abbreviations used.
If you are unsure about a stitch abbreviation, you can consult a knitting stitch dictionary or an online resource for reference. These resources provide detailed explanations and demonstrations of various stitches, helping you decode the abbreviations and understand how to execute the stitches correctly.
Decoding Pattern Repetitions
When you first look at a knitting pattern, it may seem overwhelming and confusing. However, with a little practice and understanding of the different components, you can quickly decode and read any knitting pattern. One important aspect to pay attention to is pattern repetitions. These repetitions indicate a series of stitches or rows that are repeated throughout the pattern, creating the overall design. Understanding how to identify and follow these repetitions will make reading knitting patterns much easier.
Identifying pattern repetitions: To identify pattern repetitions, look for sections in the pattern that are enclosed within brackets or parentheses. These symbols are commonly used to indicate a repetition. The number outside of the brackets or parentheses indicates how many times the enclosed section is to be repeated. For example, if you see (K2, P2) 4 times, it means you need to knit 2 stitches, purl 2 stitches, and then repeat this sequence 4 times.
Following pattern repetitions: Once you have identified the pattern repetitions, it’s important to understand how to follow them. To do this, pay attention to any instructions or stitch counts that are given within the repetition. For example, the pattern may specify to repeat the enclosed section until a certain number of stitches remain, or until a specific row number is reached. By following these instructions, you can ensure that you are correctly repeating the pattern and achieving the desired outcome.
Keeping track of pattern repetitions: When working with pattern repetitions, it can be helpful to use stitch markers or row counters to keep track of your progress. This can prevent you from losing count and ensure that you stay on track with the pattern. Additionally, it’s a good idea to make note of the number of times you have repeated a section, so you can easily refer back to it if needed.
By understanding how to decode and follow pattern repetitions, you can confidently read and knit any pattern, no matter how complex it may seem at first glance. Practice identifying and following repetitions, and soon you’ll be able to tackle even the most intricate knitting patterns with ease.
Identifying Different Types of Stitches
When reading knitting patterns, it’s important to be able to identify and understand the different types of stitches that are used. By knowing what each stitch looks like and how it is worked, beginners can follow patterns more easily and create beautiful knitted projects.
1. Knit Stitch: The knit stitch is one of the most basic stitches in knitting. It creates a smooth, V-shaped fabric. In knitting patterns, the knit stitch is typically represented by the letter “K”. To work a knit stitch, insert the right needle into the stitch on the left needle, wrap the yarn around the right needle from back to front, and pull the new loop through the old loop.
2. Purl Stitch: The purl stitch is another fundamental stitch in knitting. It creates a textured, bumpy fabric. In knitting patterns, the purl stitch is usually represented by the letter “P”. To work a purl stitch, insert the right needle into the stitch on the left needle from right to left, wrap the yarn around the right needle from front to back, and pull the new loop through the old loop.
3. Slip Stitch: The slip stitch is a technique used to move stitches from one needle to another without working them. It can be used for decorative purposes or to decrease or increase the number of stitches in a row. In knitting patterns, the slip stitch is often represented by the abbreviation “sl”. To work a slip stitch, simply insert the right needle into the stitch on the left needle as if to purl, and slide the stitch from the left needle to the right needle without knitting or purling it.
4. Decrease Stitch: Decrease stitches are used to reduce the number of stitches in a row or shape the fabric. There are different types of decrease stitches, such as knit two stitches together (k2tog), slip slip knit (ssk), or slip slip purl (ssp). Each decrease stitch creates a different effect on the fabric and is represented by its own abbreviation in knitting patterns.
5. Increase Stitch: Increase stitches are used to add stitches to a row or shape the fabric. Commonly used increase stitches include knit into the front and back of a stitch (kfb) or make one (m1). Increase stitches are usually represented by their own abbreviations in knitting patterns.
By familiarizing yourself with these different types of stitches and their abbreviations, you’ll be able to confidently read and understand knitting patterns. Practice each stitch and experiment with different combinations to create unique and beautiful knitted projects.
Reading Knitting Charts
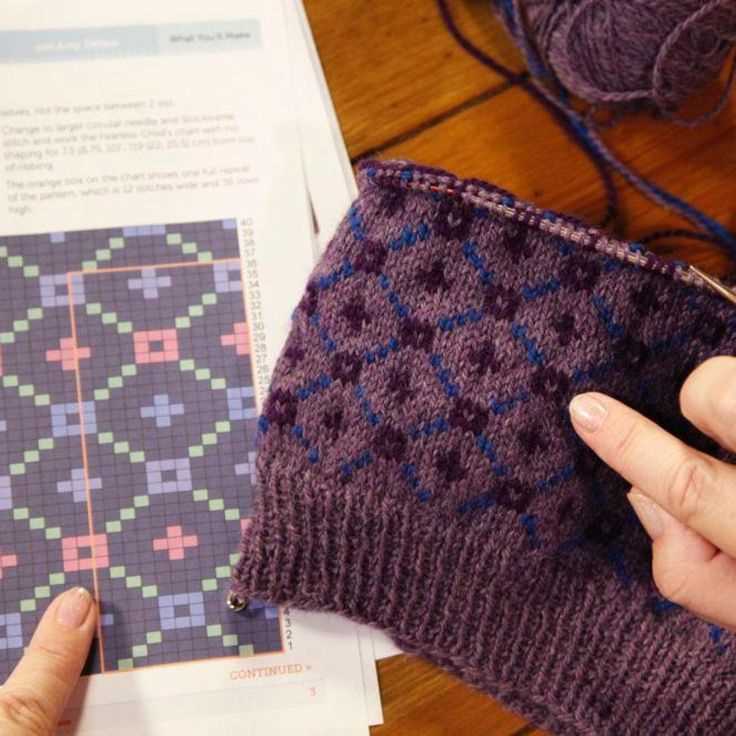
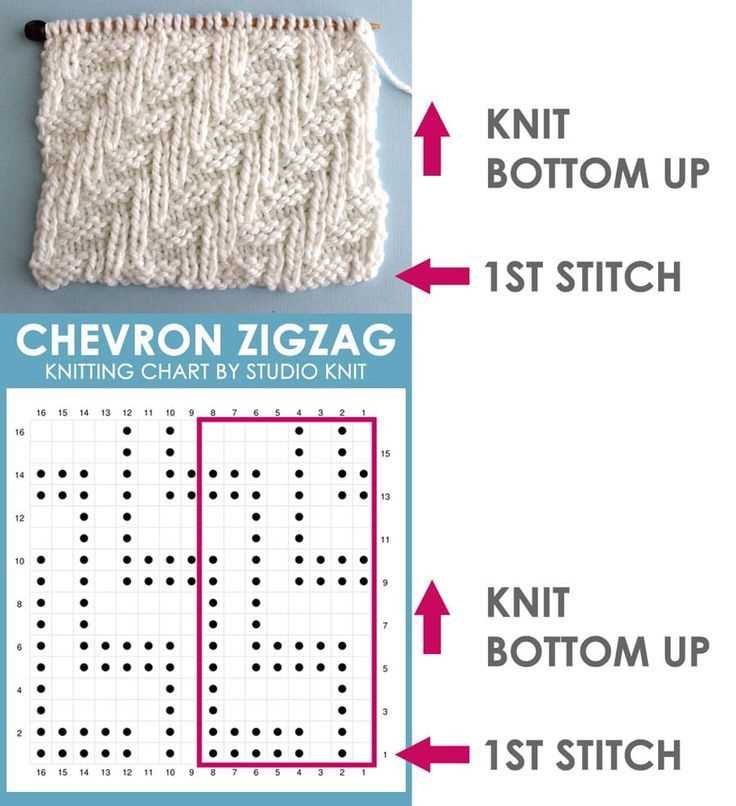
Knitting charts are visual representations of the stitches and patterns used in a knitting pattern. They are often included alongside written instructions and can be a helpful tool to understand the overall design of a project. While reading knitting charts may seem intimidating at first, with a little practice and understanding of the symbols used, they can become a valuable resource for knitters.
1. Understanding the Symbols: Each knitting chart will have a key that explains the symbols used in the chart. It is important to familiarize yourself with these symbols before starting to read the chart. Common symbols include squares to represent knit stitches, circles for purl stitches, arrows for yarn overs, and slanted lines for decreases. By understanding these symbols, you will be able to follow the chart more easily.
2. Reading from Right to Left: Knitting charts are usually read from right to left, in the same direction that you would knit. Each row of the chart represents one row of knitting. Start at the right side of the chart and follow the symbols and instructions provided to knit each stitch in the corresponding row. Once you reach the end of the row, move up to the next row on the chart.
3. Repeat and Repeat: Many knitting patterns include repeating sections or stitch patterns. When reading a knitting chart, look for sections that are enclosed within brackets or marked with repeat symbols. This indicates that the same set of stitches or pattern should be repeated a certain number of times. Pay close attention to the number of repetitions and any special instructions provided.
Reading knitting charts may take some practice, but once you become familiar with the symbols and the way charts are read, they can be a great tool for understanding knitting patterns and creating beautiful projects.
Working with knitting gauge is an essential skill for any knitter, especially beginners. The gauge refers to the number of stitches and rows in a given measurement of fabric, and it plays a crucial role in determining the size and fit of your finished project.
What is knitting gauge?
Knitting gauge is the number of stitches and rows per inch or centimeter in a knitted piece. It is typically measured using a gauge swatch, which is a small section of fabric knitted with the same yarn and needles that will be used for the project. The gauge swatch is then measured to determine the number of stitches and rows in the given measurement. This measurement is used as a guideline to ensure that the final project matches the intended size and fit.
Why is knitting gauge important?

Knitting gauge is important because it determines the size and fit of the finished project. If your gauge is too tight, meaning you have more stitches and rows per inch than the pattern calls for, your finished project will be smaller than intended. Conversely, if your gauge is too loose, with fewer stitches and rows per inch, your project will be larger. Achieving the correct gauge is crucial, especially for garments or accessories that need to fit properly.
When reading a knitting pattern, pay close attention to the suggested gauge. It is usually given as a measurement over a specific number of stitches and rows for a 4-inch / 10 cm square. The pattern will specify the recommended yarn, needle size, and any other important details to achieve the correct gauge. It is important to knit a gauge swatch before starting your project to ensure the correct gauge is achieved. This may require changing needle sizes or adjusting your tension.
Once you have completed your gauge swatch, measure it accurately to determine if your gauge matches the pattern’s requirements. Count the number of stitches and rows within the specified measurement, and compare it to the gauge stated in the pattern. If your gauge is off, you may need to make adjustments as necessary to achieve the correct gauge before continuing with your project. Remember that every knitter’s tension is different, so it is crucial to check your gauge to ensure the best results.
Interpreting Pattern Instructions

When you first begin reading knitting patterns, it can be overwhelming and confusing. However, with a little practice and understanding of the common abbreviations and symbols used in patterns, you will be able to interpret pattern instructions with ease. Here are some key tips to help you navigate knitting patterns as a beginner:
1. Read the Pattern
Start by reading through the entire pattern to get an overall understanding of the project. Pay attention to any special stitches or techniques that may be used and make note of them. This will help you anticipate any challenges and ensure you have all the necessary skills to complete the project.
2. Understand the Abbreviations
Knitting patterns often use abbreviations to save space and make instructions more concise. Familiarize yourself with common knitting abbreviations, such as “k” for knit, “p” for purl, and “yo” for yarn over. Keep a knitting abbreviations reference guide handy until you become more familiar with them.
3. Follow the Gauge
Most patterns include a gauge, which is the recommended number of stitches and rows per inch. Take the time to knit a gauge swatch to ensure your tension matches the pattern. This step is crucial to ensure the finished garment or item will turn out the correct size.
4. Take Note of Repetitions
Patterns often include repeated sections or motifs. Make sure to pay attention to the instructions for these repetitions, such as “repeat rows 1-4” or “work pattern stitch 10 times.” This will help you understand the structure of the pattern and keep track of where you are.
5. Visualize the Finished Product
As you read through the pattern, try to visualize the finished product in your mind. Understanding how the different sections of the pattern come together will help you make sense of the instructions and keep you motivated to complete the project.
Remember, practice makes perfect when it comes to reading knitting patterns. Don’t be discouraged if you don’t understand everything at first. Take your time, break down the instructions, and soon enough, you’ll be confidently knitting up beautiful projects from patterns.
Recognizing Special Knitting Techniques
When reading knitting patterns, you may encounter special techniques that are used to create different stitches or to add decorative elements to your project. It’s important to familiarize yourself with these techniques in order to successfully complete your knitting project. Here are a few common special knitting techniques to look out for:
Cables
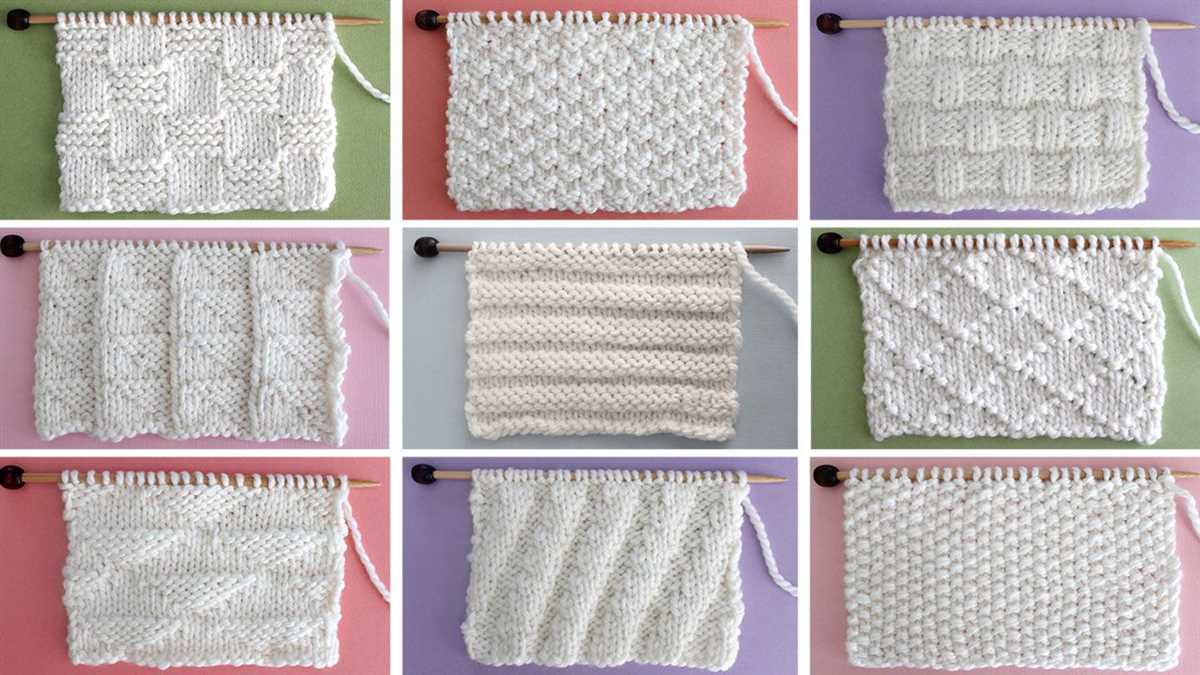

Cables are a popular technique that create a twisted, woven appearance in your knitting. They are created by knitting stitches out of order, usually by transferring some stitches onto a cable needle and holding them either in front or in back of your work while you work the other stitches. Cables can add texture and interest to your knitted fabric, and they are often used in sweaters, scarves, and blankets.
Lace
Lace knitting involves creating decorative patterns with intentional holes and yarn overs. Lace patterns are usually created by working a combination of knit and purl stitches in specific sequences. Lace knitting can be delicate and intricate, and it is often used in shawls, socks, and accessories. When reading a knitting pattern with lace instructions, pay attention to the chart or written instructions to ensure you are working the correct sequence of stitches.
Colorwork

Colorwork is a technique that involves knitting with multiple colors to create patterns and designs. This can be done using techniques such as stranded knitting, intarsia, or fair isle. Stranded knitting involves carrying multiple colors of yarn across the back of your work, while intarsia involves working with separate bobbins of yarn for each color block. Fair isle knitting typically involves working with just two colors per row, creating small, intricate patterns. Colorwork can be used to create beautiful garments, accessories, and home decor items.
By recognizing and understanding these special knitting techniques, you will be able to confidently read knitting patterns and take on a wider range of knitting projects. Remember to always read the pattern instructions carefully, and don’t be afraid to ask for help or seek out tutorials if you come across a technique that you’re unfamiliar with. With practice and patience, you’ll become a skilled knitter and be able to tackle any pattern that comes your way.
Following Color-Coded Instructions
When you first start reading knitting patterns, it can be overwhelming to see all the different symbols and abbreviations. However, many patterns now use color-coded instructions to make it easier for beginners to understand. These color-coded instructions use different colors to represent different actions or stitches, making it easier to follow along and keep track of where you are in the pattern.
For example, a knitting pattern might use the color green to indicate knit stitches and the color blue to indicate purl stitches. This makes it easy to quickly identify which stitch you should be working on at any given point in the pattern. Additionally, color-coded instructions can be helpful when working on complex patterns that involve different types of decreases or increases, as each action can be assigned a specific color for clarity.
When following color-coded instructions, it’s important to pay close attention to the key or legend provided with the pattern. This will explain which colors represent which stitches or actions, and may also include additional information about how the colors should be used. Some patterns may require you to switch colors mid-row or use multiple colors in a single row, so it’s important to familiarize yourself with the key before starting the pattern.
Overall, color-coded instructions are a fantastic tool for beginners learning to read knitting patterns. They help to simplify the pattern and make it more accessible, allowing you to focus on the stitches and techniques without getting overwhelmed by complicated symbols and abbreviations. So if you’re new to reading knitting patterns, look for patterns that use color-coded instructions to make your knitting journey a little bit easier.
Understanding Knitting Pattern Symbols
When you first look at a knitting pattern, it can be overwhelming to see all the different symbols and abbreviations. But don’t worry, once you understand what each symbol means, reading knitting patterns will become much easier.
One of the most basic symbols you’ll come across is the knit stitch symbol, which is usually represented by a small “v” or a dot. This symbol indicates that you should insert your needle into the stitch from front to back and loop the working yarn over to create a new stitch.
A different symbol you’ll often see is the purl stitch symbol, which is typically shown as a horizontal line. This symbol indicates that you should insert your needle into the stitch from back to front and loop the working yarn under to create a new stitch.
Another important symbol is the yarn over symbol, which is usually an open circle or an arrow pointing upwards. This symbol indicates that you should bring the working yarn over the needle to create an extra loop, which adds a new stitch to your knitting.
In addition to these basic stitch symbols, knitting patterns also use symbols to indicate different techniques, such as decreases, increases, and cable stitches. These symbols are typically explained in the key or glossary section of the pattern, so be sure to refer to it if you come across any unfamiliar symbols.
To make it easier to keep track of your progress, knitting patterns often include stitch markers and row indicators. Stitch markers are small rings or clips that you can place on your needles to mark specific points in your knitting. Row indicators, on the other hand, are numbers or dashes that show you how many rows you need to work before moving on to the next section of the pattern.
By familiarizing yourself with these knitting pattern symbols and understanding how to read them, you’ll be able to follow any knitting pattern with confidence. So don’t be intimidated by all the symbols – they’re just a language of their own that you’ll soon become fluent in!
Translating Pattern Terminology
When first starting out with knitting, understanding the terminology used in knitting patterns can be quite confusing. It’s important to familiarize yourself with the common terms and abbreviations used so that you can follow the instructions accurately. Here are a few key terms and their translations to help you decipher knitting patterns:
1. Cast On:
The cast on is the very first step in starting a knitting project. It is the process of creating the first row of stitches on your knitting needle. Patterns may specify a specific cast on method, such as the long-tail cast on or the cable cast on. Make sure to follow the instructions for the cast on method specified in the pattern.
2. Knit Stitch:
The knit stitch (often abbreviated as “k”) is one of the basic stitches in knitting. It involves inserting the needle through the front of the stitch, wrapping the yarn around the needle, and pulling the loop through to create a new stitch. In patterns, the term “knit” or “k” usually indicates that you need to knit a stitch on the right side of the work.
3. Purl Stitch:
The purl stitch (often abbreviated as “p”) is another basic stitch in knitting. It is the opposite of the knit stitch and creates a raised bump on the right side of the work. The purl stitch is often used to create ribbing or textured patterns. In patterns, the term “purl” or “p” usually indicates that you need to purl a stitch on the right side of the work.
4. Decrease:
Decreasing is a technique used to reduce the number of stitches in a row or round. It is typically done by knitting or purling two stitches together or by slipping stitches. The pattern will indicate how and when to decrease, usually with an abbreviation such as “k2tog” (knit two stitches together) or “ssk” (slip, slip, knit).
5. Bind Off:
Binding off is the process of finishing a knitting project by creating an edge that prevents the stitches from unraveling. It involves knitting or purling stitches and then passing one stitch over the other to create a chain-like edge. The pattern will provide instructions on how to bind off, often with the abbreviation “BO” or “bind off.”
By understanding these common terms and abbreviations used in knitting patterns, you’ll be able to confidently read and follow instructions for your knitting projects. Practice and experience will also help you become more familiar with pattern terminology over time.
Keeping Track of Rows and Rounds
When reading knitting patterns, it is important to keep track of the number of rows or rounds you have worked. This will help ensure that your project turns out as intended and prevent any mistakes or inconsistencies. There are several ways you can keep track of your progress.
Marking Rows with Stitch Markers

One method is to use stitch markers to mark the beginning of each row or round. Simply place a stitch marker in the first stitch of each new row or round, and move it up as you progress. This allows you to easily see how many rows or rounds you have completed at a glance.
Using a Row Counter

Another option is to use a row counter, which is a small device that you can attach to your knitting needles. This device allows you to manually increase the count as you complete each row or round. Some row counters even have a reset button that allows you to start counting from zero again for your next project.
Keeping a Written Record
If you prefer a more traditional method, you can keep a written record of your rows or rounds. This can be done by writing it down on a piece of paper, using a notepad or a knitting journal, or even creating a digital spreadsheet. By jotting down the number of rows or rounds you have completed, you can easily refer back to your record if needed.
No matter which method you choose, it is important to stay consistent and accurate with your counting. Double-check your counting periodically, especially when transitioning between different sections or stitch patterns in the pattern. By keeping track of your rows or rounds, you can confidently follow knitting patterns and create beautiful projects!
Tips for Troubleshooting Pattern Errors
When following knitting patterns, it’s common to encounter errors or face difficulties along the way. Here are some tips to help you troubleshoot and overcome these obstacles:
1. Double-check the pattern
Before assuming that you’ve made a mistake, verify that the pattern itself doesn’t contain errors. Look for errata or updates on the pattern designer’s website or forums dedicated to knitting. It’s always a good idea to consult other knitters who have worked on the same pattern.
2. Count your stitches and rows
Miscounting stitches or rows can easily lead to errors in your knitting. Take the time to count your stitches and rows regularly to ensure your work is on track. Use stitch markers to mark key points in the pattern and make counting easier.
3. Review abbreviations and glossary
If you are unsure about a specific abbreviation or term used in the pattern, refer to the pattern’s glossary or a knitting reference guide. Understanding the instructions correctly is crucial to following the pattern accurately.
4. Read ahead
Take the time to read through the entire pattern before starting. This will give you a better understanding of the construction and help you anticipate any potential issues. Reading ahead can also help you spot errors or confusing instructions early on.
5. Use lifelines

A lifeline is a spare piece of yarn threaded through the stitches of a particular row or round. If you make a mistake, having a lifeline in place allows you to easily rip back to that point without losing your progress. Insert a lifeline every few rows or whenever you feel unsure about your work.
6. Seek help from experienced knitters
If you’re still struggling with a pattern, don’t hesitate to seek guidance from more experienced knitters. Join knitting groups or online forums where you can ask for advice or clarification. Learning from others’ experiences and insights can be extremely helpful in troubleshooting pattern errors.
By following these tips, you’ll be better equipped to troubleshoot common pattern errors and complete your knitting projects with confidence. Remember that knitting is a skill that improves with practice, and don’t be discouraged if you encounter difficulties along the way. Happy knitting!